ERC-7586: Interest Rate Swaps
Interest rate swaps derivative contracts
Metadata
Status: ReviewStandards Track: ERCCreated: 2023-12-31
Authors
Samuel Gwlanold Edoumou (@Edoumou)
Abstract
This proposal introduces a standardized framework for on-chain interest rate swaps. The proposed standard aims to facilitate the seamless exchange of fixed and floating interest rate cash flows between parties, providing a foundation for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
Motivation
Interest Rate Swapping (IRS) denotes a derivative contract wherein two parties mutually consent to exchange a series of forthcoming interest payments based on a specified notional amount. This financial instrument serves as a strategic tool for hedging against interest rate fluctuations. The mechanism entails the utilization of a benchmark index to facilitate the exchange between a variable interest rate and a fixed rate. Despite its widespread use, there is currently an absence of a standardized framework that enables the representation of IRS contracts on blockchain platforms.
This proposal addresses this gap by establishing a consistent and transparent methodology for representing IRS contracts within the blockchain environment. By doing so, it would enhance the interoperability, security, and efficiency of interest rate swap transactions on distributed ledger technology.
Specification
The key words "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL NOT", "SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "NOT RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL" in this document are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119 and RFC 8174.
Example Flow
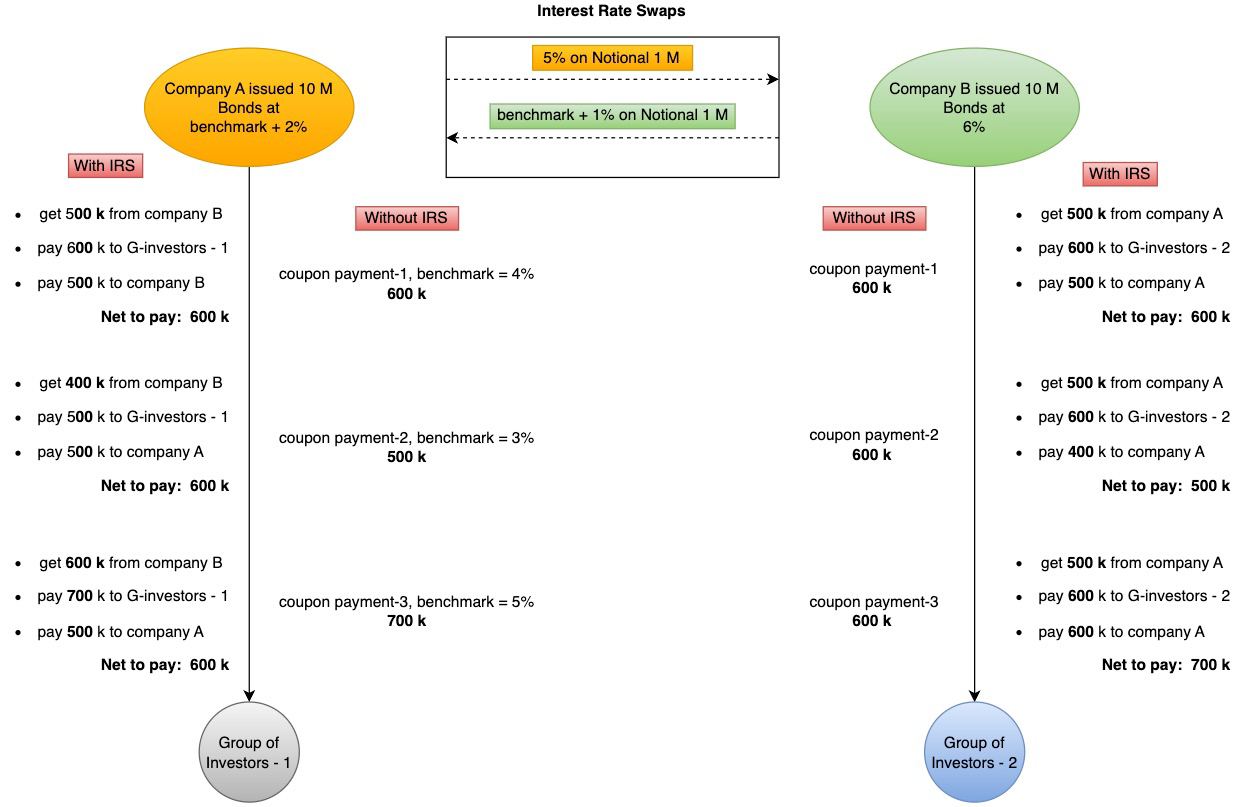
Every contract compliant with this ERC MUST implement the following interface. The contract MUST inherit from ERC-20 to tokenize the swap cash flows.
Tokenization of Swap Cash Flows
The interest payments associated with the IRS MUST be tokenized by issuing digital ERC-20 tokens to the respective parties according to the terms of the swap. Each token SHOULD represent a specific interest payment. Every time a swap happens (the swap function is called), one token MUST be burned from each party.
Rationale
This standard allows parties involved in the IRS contract to define essential parameters such as notional amount, interest rates, payment frequency, and payment dates. This flexibility accommodates a diverse range of financial agreements, catering to the unique needs of different participants.
To accommodate a wide array of use cases, the standard introduces optional features such as payment dates and manual benchmark setting. This allows parties to tailor the contract to specific requirements, while maintaining a core set of functions for essential functionality.
To ensure real-time and accurate benchmark rates, the standard integrates with oracles. Parties have the option to use oracles for fetching benchmark rates, enhancing the reliability and accuracy of interest rate calculations.
Backwards Compatibility
This standard is backward compatible with ERC-20.
Reference Implementation
The complete reference implementation can be found here.
This reference implementation serves as a foundation for the implementation of more advanced types of swaps.
Security Considerations
Security considerations of various types must be thoroughly evaluated
- Interest Rate Risk: This pertains to the potential impact of fluctuations in interest rates.
- Credit Risk: There exists the possibility that one or both parties may default on their respective responsibilities.
- ERC-20 Risks: All security aspects outlined in the ERC-20 standard must be taken into account.
Both parties must acknowledge their awareness of these security risks before proceeding with the implementation of the standard.
Copyright
Copyright and related rights waived via CC0.